rfid position detection system Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has become a key enabler for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). By taking advantage of the backscattered radio waves, the identity and position of RFID-labeled objects can be obtained simultaneously. Stay up to date with your favorite team to see if they have a chance to make the 2024 playoffs. Seven teams from each conference will make it to the postseason. Check out which teams are .
0 · rfid research topics
1 · rfid research paper
2 · rfid positioning algorithms
3 · rfid positioning
4 · radio frequency identification
5 · handheld rfid readers
1. CSL Mobile Limited is the provider of SIM Cards that may support certain Near Field Communication (NFC) services (“NFC SIM Cards”). 2. Near Field Communication services (“NFC Services”), include but are not limited to NFC .Most SIM cards aren't NFC-enabled. However, you can convert a regular SIM .

rfid research topics
Error detection built into the RFID read operation reduces the chance of a read error. RFID also has a greater reading distance than the sensing range of a proximity sensor of comparable size.It presents RFID positioning principles and techniques based on trilateration, triangulation, . Error detection built into the RFID read operation reduces the chance of a read error. RFID also has a greater reading distance than the sensing range of a proximity sensor of comparable size.It presents RFID positioning principles and techniques based on trilateration, triangulation, hybrid direction/range, radio map matching, and proximity methods and discuss potential approaches for improving positioning accuracy.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has become a key enabler for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). By taking advantage of the backscattered radio waves, the identity and position of RFID-labeled objects can be obtained simultaneously. In recent times, RFID positioning technology is a default choice for several real-time indoor tracking of people. In this article, we’ll explore how RFID location tracking works, how it enables indoor asset tracking (people monitoring), and how it compares to alternative solutions.RFID (radio-frequency identification), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. serial number) and other characteristics of an object, is an emerging positioning technology that allows for mobility tracking of objects or people.
Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) . Limited Precision: BLE is great for proximity detection but not as precise as other . In RFID systems, how to detect the position precisely is an important and challenging research topic. In this paper, we propose a range-free 2D tag localization method based on phased array. Due to its low cost and reasonable accuracy, radio-frequency identification (RFID) is promising as a supplement to GPS in connected vehicle applications at critical locations where GPS is unavailable or unreliable but the demand for real-time positioning is high.RFID positioning uses radio waves to determine the position or location of RFID tags within an area based on the principles of radio frequency communication and triangulation techniques. There are three types of RFID tags: active, passive and semi-passive.
In this article, the methodology and experiment validation to determine the position and orientation of object storage will be presented. The system consists of object storage, object shelves, RFID reader, and RFID tags. RFID tags are attached to the object storage. Error detection built into the RFID read operation reduces the chance of a read error. RFID also has a greater reading distance than the sensing range of a proximity sensor of comparable size.It presents RFID positioning principles and techniques based on trilateration, triangulation, hybrid direction/range, radio map matching, and proximity methods and discuss potential approaches for improving positioning accuracy.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has become a key enabler for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). By taking advantage of the backscattered radio waves, the identity and position of RFID-labeled objects can be obtained simultaneously. In recent times, RFID positioning technology is a default choice for several real-time indoor tracking of people. In this article, we’ll explore how RFID location tracking works, how it enables indoor asset tracking (people monitoring), and how it compares to alternative solutions.
RFID (radio-frequency identification), which uses radio waves to wirelessly transmit the identity (e.g. serial number) and other characteristics of an object, is an emerging positioning technology that allows for mobility tracking of objects or people.
Here’s a look at the main types of radio-based positioning systems commonly used: RFID, BLE, UWB, and Wi-Fi. 1. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) . Limited Precision: BLE is great for proximity detection but not as precise as other .

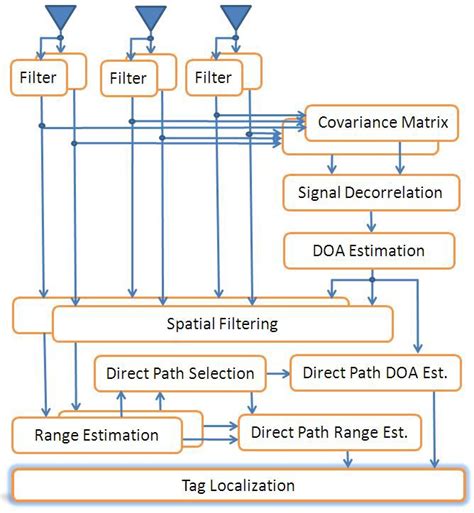
In RFID systems, how to detect the position precisely is an important and challenging research topic. In this paper, we propose a range-free 2D tag localization method based on phased array.
Due to its low cost and reasonable accuracy, radio-frequency identification (RFID) is promising as a supplement to GPS in connected vehicle applications at critical locations where GPS is unavailable or unreliable but the demand for real-time positioning is high.RFID positioning uses radio waves to determine the position or location of RFID tags within an area based on the principles of radio frequency communication and triangulation techniques. There are three types of RFID tags: active, passive and semi-passive.
rfid research paper
the real mark of the beast isn't the rfid chip
A contactless smart card is a contactless credential whose dimensions are credit card size. Its embedded integrated circuits can store (and sometimes process) data and communicate with a terminal via NFC. Commonplace uses include transit tickets, bank cards and passports. There are two broad categories of contactless smart cards. Memory cards contain non-volatile memory storage components, and perhaps some specific security logic. Contactless smart card.
rfid position detection system|handheld rfid readers